- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
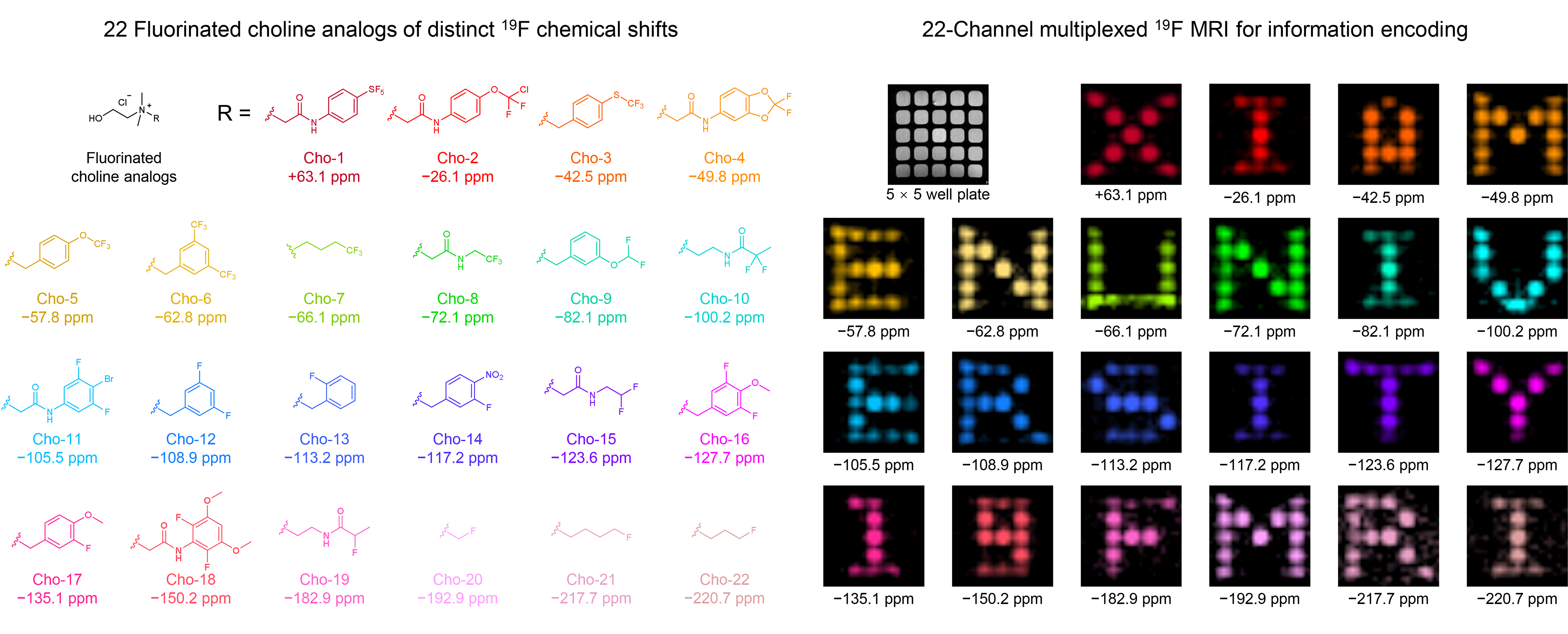
Imaging-based approaches have potential in information storage but achieving the required multiplexity can be challenging. Herein, we report the development of an MRI-based technique using 22 fluorinated quaternary ammonium derivatives with distinct 19F chemical shifts, permitting 22-channel super-multiplexed 19F MRI for information coding and processing. For details, see Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2567.
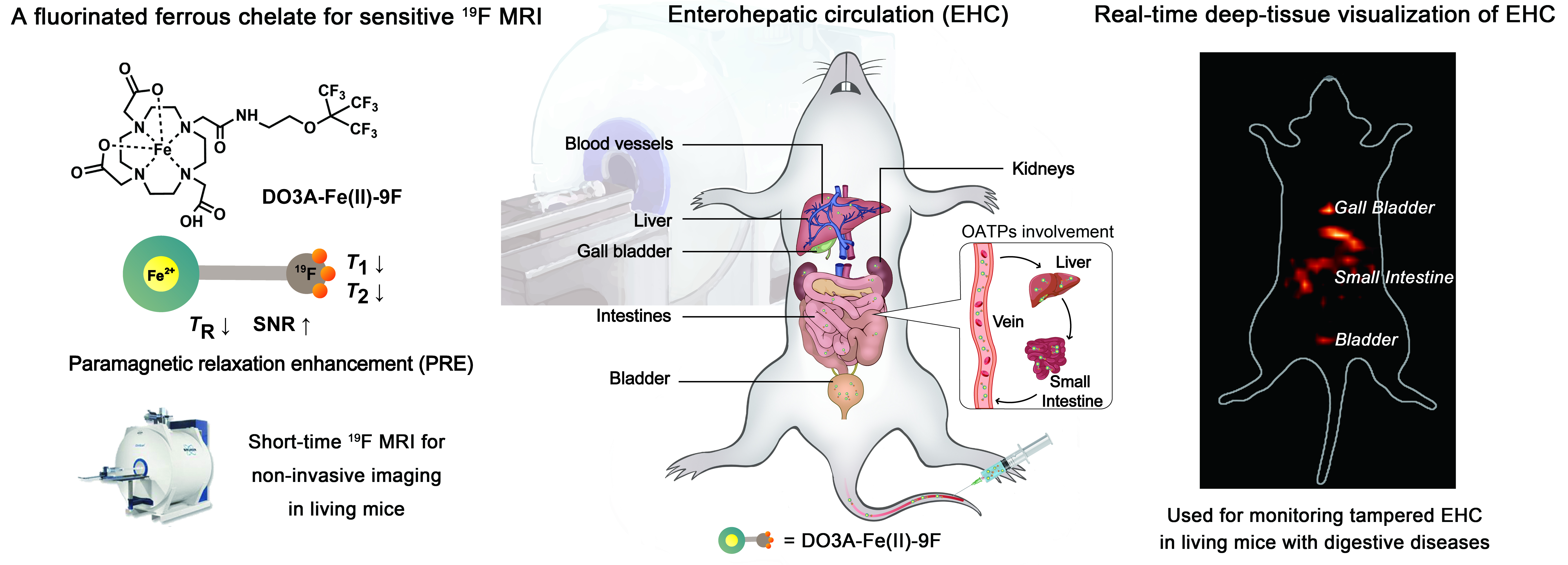
We rationally design and synthesize a ferrous chelate, DO3A-Fe(II)-9F, with high fluorine content and favorable water solubility for visualizing enterohepatic circulation (EHC) via 19F magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in vivo. Additionally, we illustrate its capacity for clearly imaging tampered EHC in the mice with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), drug-induced liver injury (DILI) or orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). For details, see Biomaterials 2025, 317, 123073.
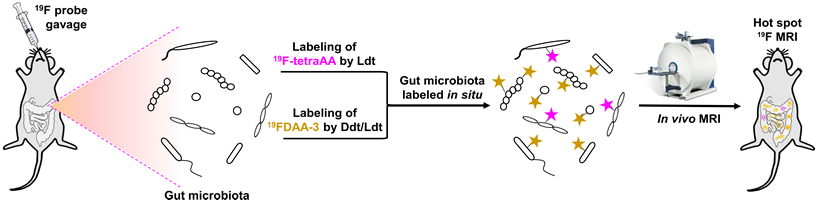
We reported a metabolic fluorine labeling (MEFLA)–based strategy for monitoring the dynamic gut microbiota via 19F magnetic resonance imaging. Our strategy holds great potential for noninvasive and real-time assessing of the metabolic activities and locations of the highly dynamic gut microbiota. For details, see Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eabg6808.
We developed a strategy called glycan MEtabolic Fluorine LAbeling (glycanMEFLA) for selectively tagging glycans of tumor cells. It allows for efficient labeling of tumor cells by fluorinated monosaccharide-based probes (Ac4ManNTfe and Ac4GalNTfa), enabling in vivo visualization of tumor cells and in situ assessment of glycosylation changes via 19F MRI. For details, see Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202313753.

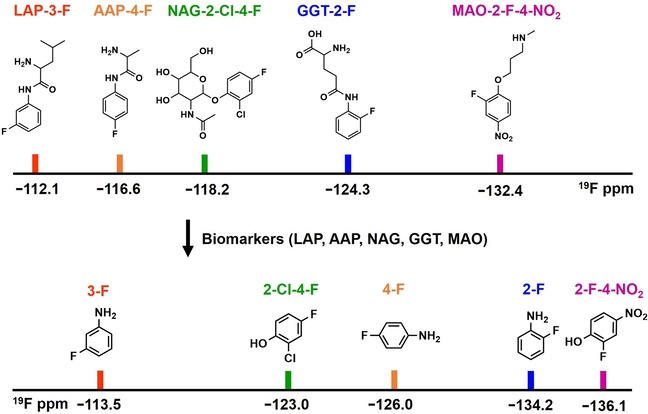
We report a set of 19F-barcoded sensors responding to different biomarkers involved in organ injury and cancer. With them, we accomplish concurrent assessment of different biomarkers in the samples collected from the mice with drug-induced liver/kidney injury or tumor. For details, see Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202211189.
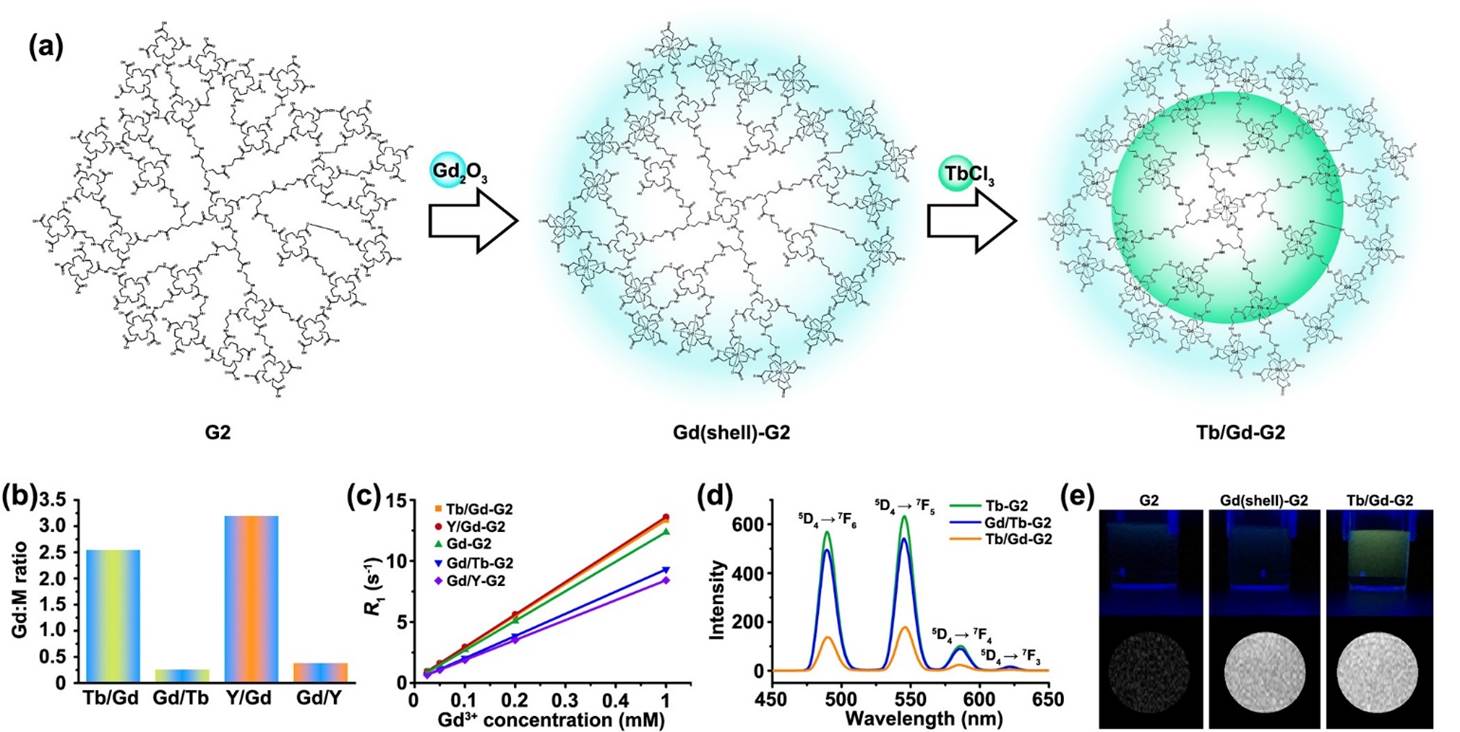
In this paper, using 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) as both a functioning unit and a constructing junction, we build a series of DOTA-branched organic frameworks with multiple chelating holes by organizing DOTA layer by layer. These giant chelators are well characterized, which reveals their nanosized and soft structures.
For details, see J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 198-206.
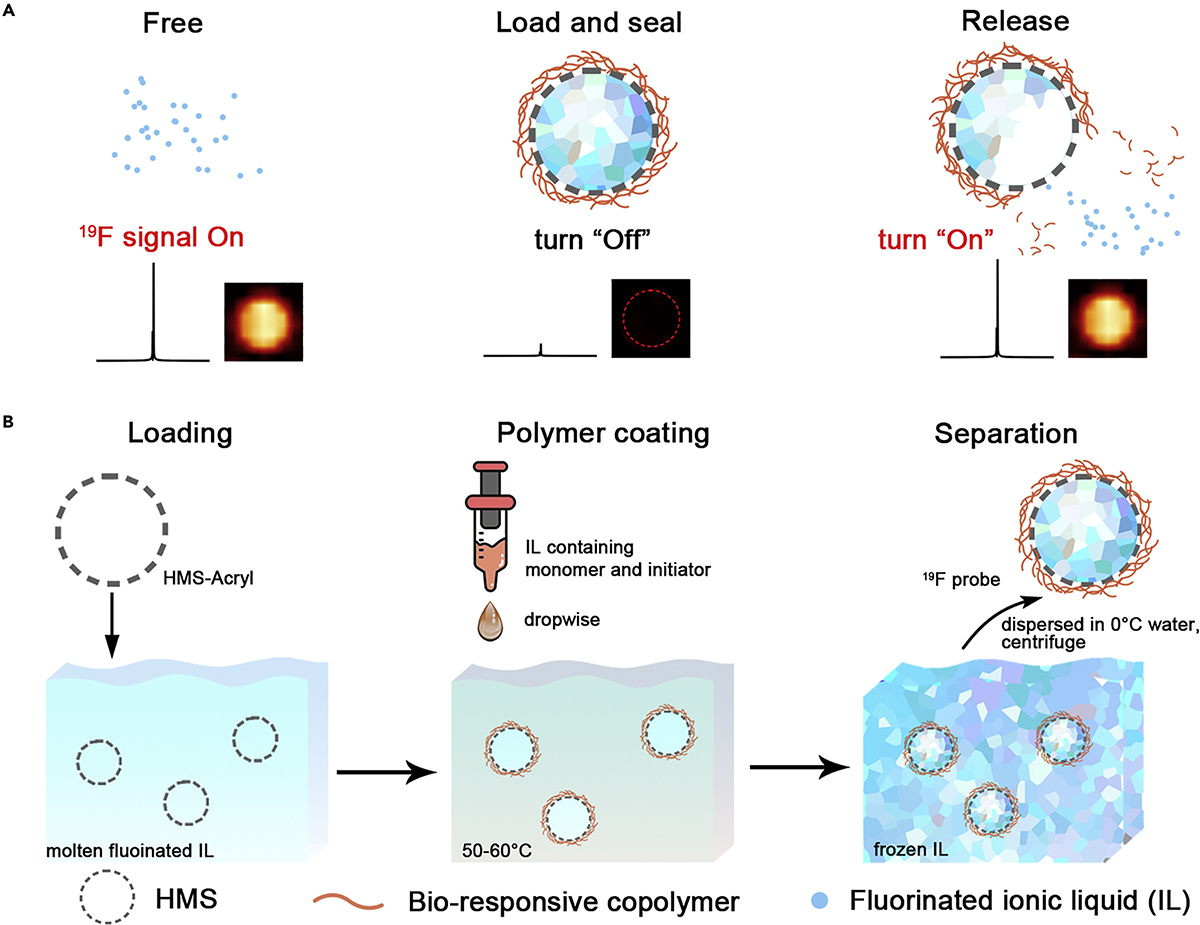
We report a fluorinated ionic liquid-based activatable 19F MRI platform for development of smart 19F probes. Several types of fluorinated ion liquids in molten state are loaded in the carriers and sealed with various stimuli-responsive diblock copolymers, leading to an “off” 19F signal.
For details, see Chem 2020, 6, 1134-1148.



Postdoctoral researchers,
graduates, and undergraduates
Welcome to join us
graduates, and undergraduates
Welcome to join us
College of Chemistry and
Chemical Engineering,
Xiamen University,
Xiamen 361005, China
Office: R528, Lu Jiaxi Building
Email: jhgao(AT)xmu.edu.cn
Phone: +86-592-2180278